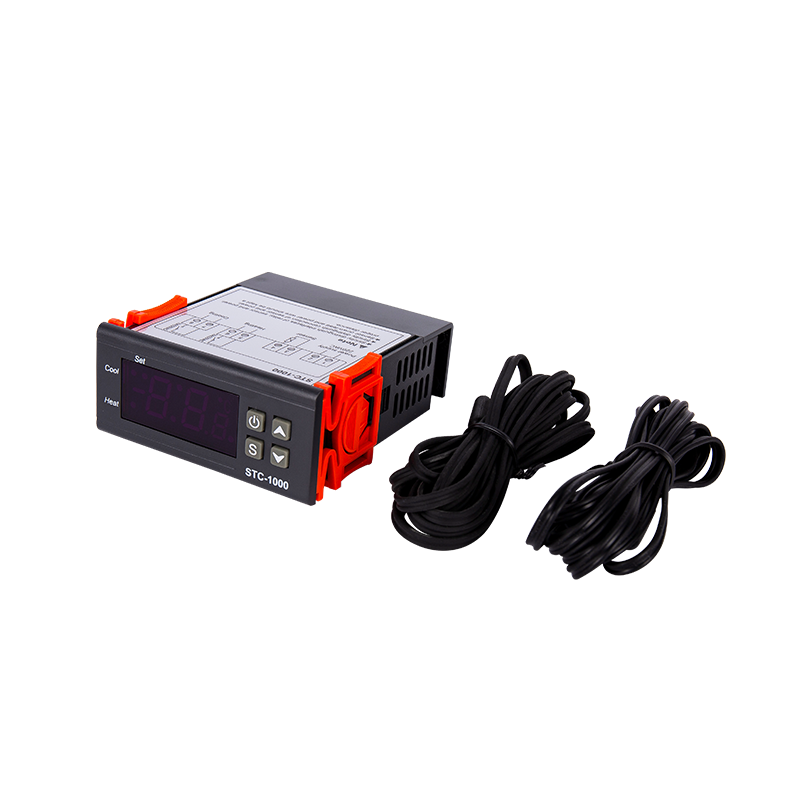
How to choose the right temperature controller for a specific application?
When choosing a temperature controller for a specific application, you need to consider several factors to ensure that the selected device can meet your needs. Here are some key steps and considerations:
1. Determine the application requirements
Temperature range: Identify the temperature range that needs to be controlled and ensure that the controller can cover this range.
Accuracy requirements: Determine the accuracy of temperature control based on the requirements of the application, such as whether ±1°C or higher accuracy is required.
Response time: Different applications require different response speeds to temperature changes. For example, some industrial processes may require a fast response, while other applications can accept a slower response.
2. Choose the control type
Control method: Decide whether to use on-off, proportional, PID control, or other control types.
On-off is suitable for simple applications that are not sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
PID control is suitable for complex applications that require high accuracy and fast response.
3. Evaluate system characteristics
Load type: Consider the thermal load characteristics of the controlled equipment (such as heaters, coolers, etc.) to determine the output capacity of the controller.
Environmental conditions: The operating environment of the temperature controller (such as humidity, vibration, dust, etc.) will also affect the selection, and a model suitable for these environmental conditions should be selected.
4. Consider output signals
Output mode: Select the appropriate output signal type, such as relay, analog output or digital output, to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
Control function: Consider whether additional functions are required, such as alarm, remote monitoring, data logging, etc.
5. Compatibility and integration
Compatibility with existing systems: Make sure the selected temperature controller can be integrated with existing sensors, actuators and other devices.
Communication protocol: If communication with other systems or devices is required, select a controller that supports the corresponding communication protocol (such as Modbus, Ethernet, etc.).